Millions of people turn to dietary supplements hoping to boost their health, immunity, sleep, memory, and physical performance. A recent Consumer Reports survey found that about 60% of U.S. adults regularly take supplements such as fish oil, probiotics, magnesium, and melatonin. However, the evidence supporting their benefits is often mixed.

For general health, fish oil may help reduce inflammation, while calcium can support bone health, especially in older adults. Probiotics may be effective for certain gut issues, but they are generally more beneficial when consumed through fermented foods.

When it comes to immunity, zinc may be helpful primarily for those who are deficient, while antioxidants tend to be more effective when obtained from a diet rich in fruits and vegetables rather than from supplements. Sleep aids like melatonin and magnesium offer modest benefits, but their long-term safety and effectiveness remain uncertain.

Nootropics such as caffeine may temporarily enhance memory, though most supplements marketed for cognitive support lack strong scientific evidence. Similarly, supplements aimed at improving skin, hair, and nails—like biotin and collagen—offer limited benefits for individuals without deficiencies.
For mood, CBD and magnesium might help ease symptoms of anxiety and depression, but lifestyle factors like quality sleep, regular exercise, and strong social connections remain more reliable. Protein powders may support muscle recovery in athletes with low dietary protein intake, while iron supplementation should be reserved for those with diagnosed deficiencies.

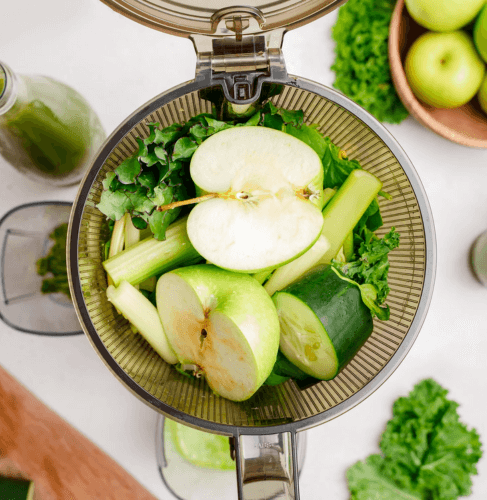
Rather than relying on supplements, the most effective way to maintain health and prevent disease is by prioritizing nutrient intake from whole, natural foods. Vitamins and minerals are absorbed most efficiently when consumed through freshly pressed juices, which offer a fast and effective delivery of essential nutrients. Ultimately, a balanced diet, regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management remain the cornerstones of lasting health.
| 🥤Nutrient | 🍽️ Food Sources | 🍹 Juice/Drink Option |
|---|---|---|
| Fish Oil (Omega-3) | Salmon, mackerel, sardines | Not ideal for juice — better with flaxseed oil smoothie or chia seed water |
| Calcium | Spinach, kale, broccoli, tofu | Kale + spinach juice, soy milk smoothie |
| Probiotics | Yogurt, kimchi, kefir | Plain yogurt smoothie, kefir drink |
| Zinc | Oysters, pumpkin seeds, chickpeas | Pumpkin seed + banana smoothie |
| Antioxidants | Blueberries, pomegranate, beets | Blueberry juice, pomegranate juice, beet smoothie |
| Melatonin | Tart cherries, banana, almonds | Tart cherry juice, banana + almond milk smoothie |
| Magnesium | Spinach, avocado, banana | Spinach + banana smoothie, avocado shake |
| Caffeine (Nootropic) | Coffee, green tea | Cold brew coffee, matcha latte |
| Biotin | Eggs, nuts, avocado | Avocado + mixed nuts smoothie |
| Collagen | Chicken feet, pork skin, fish skin | Not suitable for juice — recommend collagen peptide drink |
| CBD | Extracted from hemp oils | CBD drops in lemon water |
| Protein | Chicken breast, tofu, beans | Soy milk + nuts protein smoothie |
| Iron | Spinach, lentils, red meat | Spinach + apple juice, lentil smoothie |
| Fiber | Oats, apple, chia seeds | Oat + apple smoothie, chia seed lemon water |
| Green Tea Extract | Green tea | Matcha smoothie, green tea latte |
👩All articles are written by Ph.D. Lee, Principal Researcher, and Ph.D. Son, Senior Researcher at the Kuvings Bio Research Institute.